Based on the Usda Food Security Classifications, How Would You Categorize the Family?
Scientific discipline and History of GMOs and Other Food Modification Processes
Feed Your Mind Chief Page
en Español (Spanish)
How has genetic engineering changed plant and animal breeding?
Did you know?
Genetic engineering is oftentimes used in combination with traditional breeding to produce the genetically engineered constitute varieties on the market today.
For thousands of years, humans have been using traditional modification methods like selective breeding and cross-breeding to breed plants and animals with more desirable traits. For case, early farmers developed cross-breeding methods to grow corn with a range of colors, sizes, and uses. Today's strawberries are a cantankerous betwixt a strawberry species native to North America and a strawberry species native to South America.
Near of the foods we swallow today were created through traditional breeding methods. Simply changing plants and animals through traditional breeding tin can take a long time, and information technology is difficult to make very specific changes. Afterward scientists developed genetic engineering science in the 1970s, they were able to make like changes in a more specific way and in a shorter amount of time.
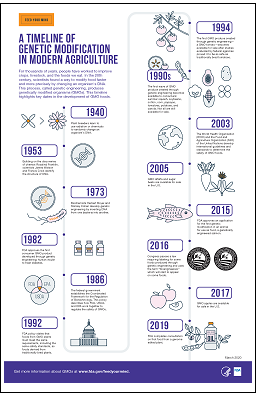
A Timeline of Genetic Modification in Agriculture
A Timeline of Genetic Modification in Modernistic Agriculture
PDF 152KB
Circa 8000 BCE: Humans utilise traditional modification methods like selective breeding and cantankerous-breeding to breed plants and animals with more desirable traits.
1866: Gregor Mendel, an Austrian monk, breeds two different types of peas and identifies the basic procedure of genetics.
1922: The kickoff hybrid corn is produced and sold commercially.
1940: Plant breeders learn to employ radiation or chemicals to randomly modify an organism's Dna.
1953: Building on the discoveries of chemist Rosalind Franklin, scientists James Watson and Francis Crick place the structure of DNA.
1973: Biochemists Herbert Boyer and Stanley Cohen develop genetic engineering by inserting Deoxyribonucleic acid from one leaner into another.
1982: FDA approves the first consumer GMO product developed through genetic applied science: homo insulin to treat diabetes.
1986: The federal authorities establishes the Coordinated Framework for the Regulation of Biotechnology. This policy describes how the U.S. Nutrient and Drug Administration (FDA), U.S. Ecology Protection Agency (EPA), and U.Southward. Section of Agriculture (USDA) work together to regulate the safety of GMOs.
1992: FDA policy states that foods from GMO plants must meet the aforementioned requirements, including the same safe standards, every bit foods derived from traditionally bred plants.
1994: The get-go GMO produce created through genetic engineering—a GMO lycopersicon esculentum—becomes available for auction after studies evaluated by federal agencies proved it to be every bit safety equally traditionally bred tomatoes.
1990s: The start moving ridge of GMO produce created through genetic engineering becomes bachelor to consumers: summer squash, soybeans, cotton fiber, corn, papayas, tomatoes, potatoes, and canola. Not all are still available for auction.
2003: The Globe Health System (WHO) and the Food and Agronomics Arrangement (FAO) of the United Nations develop international guidelines and standards to make up one's mind the safety of GMO foods.
2005: GMO alfalfa and sugar beets are available for sale in the United states.
2015: FDA approves an awarding for the first genetic modification in an animal for use every bit food, a genetically engineered salmon.
2016: Congress passes a police requiring labeling for some foods produced through genetic engineering and uses the term "bioengineered," which volition start to appear on some foods.
2017: GMO apples are available for sale in the U.S.
2019: FDA completes consultation on first food from a genome edited plant.
How are GMOs fabricated?
"GMO" (genetically modified organism) has become the common term consumers and popular media use to describe foods that take been created through genetic engineering. Genetic technology is a process that involves:
- Identifying the genetic data—or "gene"—that gives an organism (found, animate being, or microorganism) a desired trait
- Copying that information from the organism that has the trait
- Inserting that data into the DNA of some other organism
- And then growing the new organism
How Are GMOs Made? Fact Sheet
Making a GMO Institute, Pace by Step
The following instance gives a general idea of the steps it takes to create a GMO plant. This example uses a type of insect-resistant corn called "Bt corn." Keep in mind that the processes for creating a GMO found, animal, or microorganism may exist different.
Identify
To produce a GMO plant, scientists start identify what trait they desire that plant to have, such as resistance to drought, herbicides, or insects. Then, they find an organism (plant, animal, or microorganism) that already has that trait inside its genes. In this instance, scientists wanted to create insect-resistant corn to reduce the demand to spray pesticides. They identified a factor in a soil bacterium called Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), which produces a natural insecticide that has been in use for many years in traditional and organic agriculture.
Re-create
After scientists observe the cistron with the desired trait, they copy that gene.
For Bt corn, they copied the gene in Bt that would provide the insect-resistance trait.
Insert
Next, scientists use tools to insert the cistron into the DNA of the plant. By inserting the Bt factor into the Deoxyribonucleic acid of the corn establish, scientists gave it the insect resistance trait.
This new trait does non change the other existing traits.
Grow
In the laboratory, scientists grow the new corn plant to ensure it has adopted the desired trait (insect resistance). If successful, scientists first grow and monitor the new corn plant (at present called Bt corn because it contains a gene from Bacillus thuringiensis) in greenhouses and then in small-scale field tests before moving information technology into larger field tests. GMO plants become through in-depth review and tests before they are ready to exist sold to farmers.
The entire process of bringing a GMO found to the market place takes several years.
Learn more than about the process for creating genetically engineered microbes and genetically engineered animals.
What are the latest scientific advances in establish and animal convenance?
Scientists are developing new ways to create new varieties of crops and animals using a process called genome editing. These techniques can make it easier and quicker to brand changes that were previously done through traditional breeding.
There are several genome editing tools, such as CRISPR. Scientists can use these newer genome editing tools to make crops more than nutritious, drought tolerant, and resistant to insect pests and diseases.
How GMOs Are Regulated for Food and Plant Safety in the United States
GMO Crops, Animal Food, and Across
How GMO Crops Impact Our World
www.fda.gov/feedyourmind
Source: https://www.fda.gov/food/agricultural-biotechnology/science-and-history-gmos-and-other-food-modification-processes






0 Response to "Based on the Usda Food Security Classifications, How Would You Categorize the Family?"
Post a Comment